What is Norwegian Crusted Scabies?
Crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, is a severe & highly contagious form of scabies, characterized by thick crusts of the skin that contain thousands or even millions of scabies mites and eggs; associated with psoriasiform scaling patches. these microscopic mites burrow into the skin of the infested person and colonize the epidermis.
However, Norwegian scabies is an infrequent form of infestation by “Sarcoptes scabiei var Hominis”; that can occur in some patients who have a weak immune system, or who do not scratch because of an absence of pruritus or immobility, such as the elderly, disabled, patients with sensory neuropathy, paresis or debilitated.
Why do they call it Norwegian scabies?
Crusted scabies is also called Norwegian scabies because the first scientifically described cases of this condition were reported in Norway by “
Daniel Cornelius Danielssen” and “
Carl Wilhelm Boeck” ( Norwegian physician and dermatologist) in 1848, who believed it to be a form of leprosy, which was endemic in Norway at that time.
Later, in 1852 “Ferdinand Hebra” published a short paper on the subject, who observed a similar case during his visit to Oslo, Norway, and gave the disease the name “scabies norvegica Boeckii” or “Boeck’s Norwegian scabies”.
However, it is preferable to call this disease Crusted scabies because it is more clinically descriptive. Also, since it occurs worldwide not only in Norway or doesn’t affect only the people of Norwegian descent.
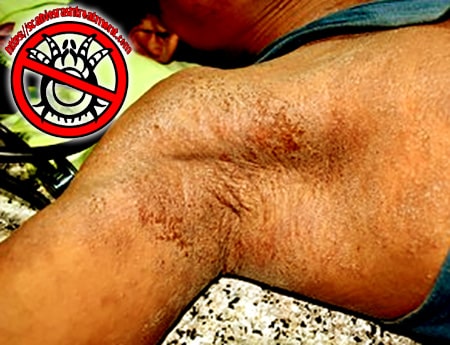
What does crusted scabies look like?
Distinctive and early signs of Norwegian/crusted scabies include red patches on the skin, these spots later develop into thick plaques. Next, the patches on the skin of people with crusted scabies looks like gray, thick, and crumbly when touched.
Lesions appear on: The scalp, back, face, elbows, knees, palms, and soles of the feet…
Why is crusted Norwegian scabies more contagious?
As we have already mentioned, the infection with crusted Norwegian scabies is only the result of not treating the normal scabies, for people with a weak immune system (such as elderly and infants…). The weakness of the immune system leaves the infected person’s body without resistance, So the number of scabies mites continues to increase in the host’s body to reach more than two million mites; persons with Norwegian scabies are extremely contagious to others, since they are infested with such large amounts of mites and eggs.
Be careful when handling an infected person. Crusted scabies can be spread by:
- Direct contact (handshake).
- Also, through contaminated items such as clothing, bedding, and furniture used by the infected person.
What is the difference between scabies and crusted scabies?
Crusted scabies vs scabies
Crusted scabies is the severest and the most contagious type of scabies. The difference between normal scabies and crusted scabies is that the crusted Norwegian scabies is characterized by a much larger number of scabies mites and eggs present in the skin of the infested person. Also, unlike regular scabies, the mites are present almost in all parts of the body, including the head, nails, neck, and scalp.
However, strangely, the rash associated with Norwegian scabies commonly doesn’t itch.
How long does it take for scabies to become crusted scabies?
Crusted scabies is a complication of normal scabies if not treated properly after the skin reaction. In some cases, it can take only a few weeks for regular scabies to become CS if the infested person is “vulnerable”. We’re talking here about:
- People with a weak immune system,
- Neurological disorders,
- Down’s syndrome,
- HIV or AID’s,
- Also, if the patient is an infant, an elderly, or a pregnant woman…
On the other hand, scientists have proven that a strong immune system breaks the reproduction cycle of scabies mites.
Norwegian scabies signs and symptoms include:
- The skin crusts are the most important sign of crusted scabies. A very thick crusts on the skin because of the large number of mites.
- Itching is one of the most common symptoms, The intense itching could keep a person awake all night.
- Hive-like bumps on the skin.
- Sores: Scratching the itchy rash can cause sores.
Crusted scabies or something else?
How do I know if I have crusted scabies or dry skin or eczema?
To answer that question: if you suspect it is scabies or something else, no doubt you need to see a doctor, you absolutely need a diagnosis from your primary health care provider to determine your condition exactly and correctly; in order to find a treatment plan that works for your skin. For that, the dermatologist will take a scraping from your skin as a sample for testing to confirm Norwegian scabies or dry skin, eczema, or something else…because They can look similar, but they are different conditions.
PS:
Don’t ask for your diagnosis online or through an app, and don’t rely on other people’s experiences.
Scabies vs Eczema:
Scabies is an itchy rash caused by an allergic response to the infestation of small, burrowing, 8 legged mites living on your skin. It’s also highly contagious.
On the other hand, Eczema is a skin irritation that gives your skin a rash-like appearance. The specialists don’t know the exact cause, they suspect that eczema is triggered by genetic or environmental factors. However, the good news here is that eczema is not contagious at all.
Can crusted scabies kill you?
Crusted scabies-related deaths are uncommon. Norwegian scabies can be treated by following the doctor’s prescriptions, which often consist of creams or/and tablets. Yet, the disease could lead to fatal complications in certain patients, if untreated this condition has high mortality due to secondary sepsis. With outbreaks of scabies may contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease and subsequent renal failure source.
Is crusted scabies curable?
Medical scientific research has made the most incurable diseases treatable, and scabies is not an exception. Norwegian scabies can be cured, Even though, it is a hyper-infestation with millions of mites. In order to cure scabies, it is important to follow the dermatologist’s prescription. Until the symptoms of the infestation disappear permanently, to prevent re-infestation.
How do you get rid of crusted Norwegian scabies?
In order to get rid of Crusted Norwegian scabies, the United States Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends applying Topical 5% permethrin cream or topical 5% benzoyl benzoate, every day for a week. Then, apply topical medication or the combined treatment based on a topical and an oral medication repeatedly, two times weekly, week by week until cure.
Ordinarily, the dermatologist may instruct patients with crusted scabies to remove scaling skin, with the aim that topical creams can penetrate smoothly into the skin.
How long does it take to treat crusted scabies?
By all the odds, nobody can tell exactly how long it takes to cure scabies, it depends on many things including: the health and age of the patient and the state of his immune system. Also, when the patient has sought medical expertise, And if he follows the dermatologist instructions. It can take few weeks to several months to fully recover.
Even though, after taking the right treatment, the skin should heal within one month. Yet, expect that the rash and itch may worsen during treatment.
How do you get rid of crusted scabies naturally?
In short, there is no scientific evidence of the effectiveness of home treatment remedies to cure crusted Norwegian scabies. Although some natural treatments have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and analgesic properties. Crusty scab is a serious condition and should be monitored by a specialist.