How is scabies diagnosed?
Delving into the diagnosis of scabies, this article sheds light on the essential techniques for identifying and managing this bothersome skin condition. When diagnosing scabies, medical practitioners follow a set of procedures to confirm the presence of scabies mites and their eggs. These procedures may include physical examination, dermatoscopy, skin scraping, and the distinctive borrow-ink test (BIT). Now, are you wondering how scabies are diagnosed? Join us on this exploration as we unveil the secrets of scabies diagnosis, guiding you through the process. Let’s unravel the mysteries together!
Recognizing Scabies Symptoms
Identifying scabies symptoms is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. The primary sign is persistent itching, often more noticeable at night. Notably, scabies bumps are a distinct indication, along with the formation of skin burrows, providing tangible evidence of scabies mites’ presence. Scabies bites causing severe and persistent itching raise concerns about a potential infestation.
Symptoms play an important role in the diagnosis process. If you’re pondering the question, “How do I test if I have scabies?” The following paragraph will delve into the various methods dermatologists employ to confirm whether it’s a scabies infestation or something else.
How do scabies get diagnosed?
Embarking on a scabies diagnosis, let’s delve into the methods healthcare professionals use to confirm this skin health condition. Join us as we explore diagnostic intricacies, shed light on tools for a conclusive understanding of scabies, and pave the way for effective treatment.
-
-
Insights from the Physical Examination:
-
In scabies diagnosis, doctors conduct a thorough physical examination with attention to detail. They are inspecting for signs like tiny burrows, red bumps, or rashes. Simultaneously, they inquire about symptoms, such as intense nocturnal itching and a distinctive rash from scabies bites. This approach helps doctors confirm scabies during an examination. Additional symptoms, including pimple-like irritations, sores, or symptom exacerbations in specific body areas, may raise suspicion. If uncertainty persists, doctors may need additional diagnostic methods beyond the initial examination to reach a definitive diagnosis.
-
-
Dermatoscopy: An In-Depth Exploration in Scabies Diagnosis:
-
In scabies diagnosis, dermoscopy is decisive. Employing a dermatoscope, doctors magnify the skin, honing in on microscopic signs like burrows or mite tunnels. This precise approach significantly enhances diagnostic accuracy, especially for subtle symptoms that might be missed during a routine physical examination. Additionally, dermatoscopy not only allows for a more comprehensive examination but also empowers doctors to scrutinize the skin at a microscopic level, ensuring the identification of scabies indicators with higher precision. This modern diagnostic instrument, equipped with high-quality magnifying lenses and a powerful lighting system, streamlines the confirmation of scabies, reducing the time required compared to traditional identification methods.
-
Scabies Diagnosed through Skin Scraping
The skin scraping test is a widely used and highly effective method for diagnosing scabies. This technique involves delicately scraping the skin’s surface in symptomatic areas, enabling a detailed microscopic examination. It helps accurately identify scabies mites, their eggs, and scybala. The procedure includes applying a drop of mineral oil over the burrow and then carefully scraping longitudinally and laterally with a scalpel. This method proves especially valuable when burrows are not visibly apparent, significantly enhancing diagnostic precision. Furthermore, health professionals widely regard the microscopic examination of skin scrapings with dermoscopy as the gold standard for scabies diagnosis, as it significantly enhances diagnostic precision.
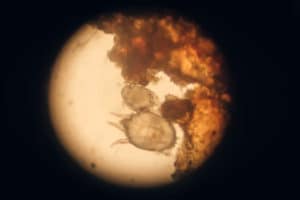
Source: shutterstock.com
-
Skin Biopsy:
To diagnose scabies, doctors use a meticulous method called skin biopsy, where they extract a small piece of skin tissue for thorough analysis. Targeting areas with visible lesions or burrows, this in-depth examination reveals scabies mites, eggs, or other indicators. The key point is that it provides essential insights for precise diagnosis, particularly when a more profound understanding is necessary. Notably, the key distinction from skin scraping lies in the depth of tissue collection, with biopsy reaching deeper layers for a more comprehensive perspective on scabies infestation.
-
Revealing the Scabies Borrow Ink Test Diagnosis:
The Burrow-Ink Test (BIT) is a reliable method for diagnosing scabies. Using ink, typically from a wide felt-tip pen (preferably blue or green), doctors apply a scabies ink test over suspected burrows. After using an alcohol swab to remove the surface ink, a dark and irregular line remains, highlighting the burrow. Upon examining the skin using a magnifier or dermatoscope, the intricate paths created by scabies mites can be observed. While valuable for visualizing burrows, the Burrow-Ink Test may not always detect the mites themselves. However, when combined with other diagnostic methods, like dermatoscopy or skin scraping, it offers a comprehensive view of scabies infestation. This aids doctors in confirming the diagnosis and tailoring treatment for individuals with scabies.

Performing an Ink Test for Scabies at Home
Embarking on an ink test for scabies at home may seem enticing. The process involves choosing a suspect skin area, coloring it with an ink pen or marker, waiting for 10 seconds, and gently wiping the stained area with alcohol-soaked gauze to identify the characteristic zigzag line where the mite has tunneled. However, it is important to emphasize that trying this ink test for scabies at home is not recommended. Due to the potential dangers of self-diagnosis, including delayed appropriate professional diagnosis, treatment, and potential harm to the skin, if you suspect scabies, seeking professional consultation from a dermatologist is advisable for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Confirming Scabies, What else can be mistaken for scabies?
In previous sections, we have studied the detailed techniques that dermatologists use to diagnose scabies. Yet, navigating scabies diagnosis goes beyond tool understanding; it’s about decoding the subtle nuances that differentiate it from other skin conditions. Additionally, many skin diseases have similar symptoms, making the diagnostic process even more complicated. Here’s a concise list:
-
Eczema (Dermatitis):
- Itching, redness, and rash characterize eczema, often leading to potential misdiagnosis due to shared visual cues.
-
Psoriasis:
- Psoriasis presents with skin redness, itching, and scales, sharing symptomatic similarities with scabies.
-
Contact Dermatitis:
- A red, itchy rash arising from irritant or allergen contact can resemble scabies, causing diagnostic challenges.
-
Folliculitis:
- Inflamed hair follicles result in red bumps, potentially confusing them with scabies burrows.
-
Impetigo:
- Red sores or blisters stemming from a skin infection may mimic scabies, posing a diagnostic puzzle.
This concise list covers conditions that might resemble scabies at first glance, emphasizing the importance of a sharp diagnosis.
To properly diagnose and treat any skin-related issues, it is best to consult a dermatologist who possesses the necessary diagnostic tools and knowledge. This proactive approach ensures the best treatment for scabies rash.
Scabies Diagnosis Flowchart
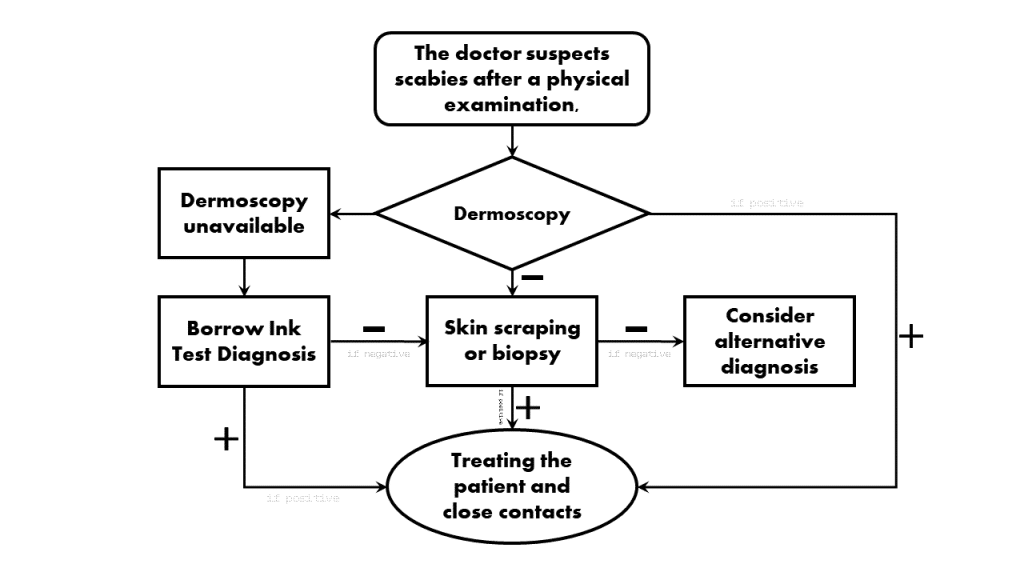
In the process of diagnosing scabies, the doctors typically follow this algorithm for diagnosing scabies. They begin with dermatoscopy after a physical examination. A positive result prompts immediate treatment for the patient and close contact. If dermatoscopy isn’t an option, the next step is the BORROW INK test. A positive outcome triggers prompt treatment. If the ink test is negative, the doctor turns to skin scraping or biopsy. A positive result here confirms the presence of scabies mites, leading to treatment for the patient and close contacts. For a negative biopsy or scraping, the doctor explores alternative diagnoses for conditions resembling scabies.
Resources :
- “Dermatology: Illustrated Study Guide and Comprehensive Board Review” by Sima Jain A comprehensive guide covering various dermatological topics, including diagnostic methods.
- “Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine,” edited by Lowell Goldsmith, Stephen Katz, and Barbara A. Gilchrest Chapter 208; renowned dermatology reference.